Terminology in Thermodynamics
Terminology in Thermodynamics: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Hess's Law of Heat Summation, Applications of Hess's Law of Heat Summation, and Born-Haber Cycle.
Important Questions on Terminology in Thermodynamics
Which of the following are not state functions?
During isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, its
For a cyclic process, which of the following is not true?
Three separate reversible processes are carried out with mole of an ideal gas initially at STP. In these processes, the pressure () is measured while increasing any one of the quantities volume (), temperature () and number of moles , keeping the other two constant. Plots of versus are found to be linear, where or or . For the processes and , the numerical values of the slopes and of the versus plots are found to follow the order , respectively. The correct statement(s) about these processes is/are
Consider a cyclic process for a system. Among the following, the combination of steps that can never lead to this cyclic process is
In thermodynamics, a process is called reversible when.
Out of molar entropy specific volume heat capacity volume extensive properties are
How is potential energy of water is converted into electrical energy?
When a book is dropped, its _____ energy is transformed into kinetic energy.
Write an example for the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy.
The diagram shows the pressure and volume relationship for one cycle of operation of an engine.
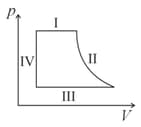
Which of the labelled parts of the cycle identify isobaric changes and adiabatic changes of state?
Which of the following option is correct match for extensive and intensive property:
Which of the following pairs belongs to extensive property?
Which of the following statements is true for an open system?
Work done by an ideal gas at a constant volume is__________
Which of the following is an extensive property?
Which of the following variables control the physical properties and behaviour of the gas?
When heat is added to a gas constantly, it results in
An isolated system is that system in which:
As shown in the figure, the walls of the beakers will act as_____ ?

